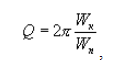-
1 régime maximum continu
максимальный продолжительный режим работы ГТД
максимальный продолжительный режим
Установившийся режим работы ГТД, характеризуемый пониженными по сравнению с максимальным режимом значениями частоты вращения ротора (роторов) и температуры газа перед турбиной, при которых двигатель может работать с ограниченной по времени общей наработкой.
Примечания
1. Параметры ГТД на максимальном продолжительном режиме имеют индекс «mах пр».
2. Для некоторых ГТД частота вращения ротора может оставаться неизменной.
[ ГОСТ 23851-79]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
245. Максимальный продолжительный режим работы ГТД
Максимальный продолжительный режим
D. Maximaler Dauerbetriebszustand
Е. Maximum continuons rating
F. Régime maximum continu
Установившийся режим работы ГТД, характеризуемый пониженными по сравнению с максимальным режимом значениями частоты вращения ротора (роторов) и температуры газа перед турбиной, при которых двигатель может работать с ограниченной по времени общей наработкой.
Примечания:
1. Параметры ГТД на максимальном продолжительном режиме имеют индекс «max пр».
2. Для некоторых ГТД частота вращения ротора может оставаться неизменной.
Источник: ГОСТ 23851-79: Двигатели газотурбинные авиационные. Термины и определения оригинал документа
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > régime maximum continu
-
2 régime de fonctionnement maximal
максимальный режим работы ГТД
максимальный режим
Установившийся режим работы ГТД, характеризуемый максимальной тягой (мощностью) на земле или в полете в течение ограниченного времени.
Примечание
Параметры ГТД на максимальном режиме имеют индекс «mах».
[ ГОСТ 23851-79]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
243. Максимальный режим работы ГТД
Максимальный режим
D. Maximale Betriebszustand
Е. Maximum rating
F. Régime de fonctionnement maximal
Установившийся режим работы ГТД, характеризуемый максимальной тягой (мощностью) на земле или в полете в течение ограниченного времени.
Примечание. Параметры ГТД на максимальном режиме имеют индекс «max».
Источник: ГОСТ 23851-79: Двигатели газотурбинные авиационные. Термины и определения оригинал документа
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > régime de fonctionnement maximal
-
3 régime de fonctionnement du TRPC (TRDFPC) à pleine réchauffe
полный форсированный режим работы ТРДФ (ТРДДФ)
полный форсированный режим
Ндп. полный форсажный режим работы ТРДФ (ТРДДФ)
Форсированный режим работы ТРДФ (ТРДДФ), характеризуемый максимальным расходом топлива в форсажной камере сгорания при максимальных частоте вращения ротора (роторов), двигателя и температуре газа перед турбиной.
Примечание
Параметры ГТД на полном форсированном режиме имеют индекс «ПФ».
[ ГОСТ 23851-79]Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Тематики
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
250. Полный форсированный режим работы ТРДФ (ТРДДФ)
Полный форсированный режим
Ндп. Полный форсажный режим работы ТРДФ ( ТРДДФ)
D. Betriebszustand mit maximaler Nachverbrennung
E. Augmented turbojet (turfofan) maximum afterburning rating
F. Régime de fonctionnement du TRPC (TRDFPC) á pleine réchauffe
Форсированный режим работы ТРДФ (ТРДДФ), характеризуемый максимальным расходом топлива в форсажной камере сгорания при максимальных частоте вращения ротора (роторов), двигателя и температуре газа перед турбиной.
Примечание. Параметры ГТД на полном форсированном режиме имеют индекс «ПФ».
Источник: ГОСТ 23851-79: Двигатели газотурбинные авиационные. Термины и определения оригинал документа
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > régime de fonctionnement du TRPC (TRDFPC) à pleine réchauffe
-
4 régime maximum continu
сущ.тех. номинальный режимФранцузско-русский универсальный словарь > régime maximum continu
-
5 régime maximum du réacteur
Французско-русский универсальный словарь > régime maximum du réacteur
-
6 facteur de régime cyclique
коэффициент циклической токовой нагрузки (кабелей)
Коэффициент, на который может быть умножен номинальный ток установившегося режима, соответствующий коэффициенту нагрузки 100 %, для получения допустимого пикового значения тока в течение суточного цикла, при котором температура токопроводящей жилы в течение этого цикла достигает, но не превышает максимально допустимое значение
[IEV number 461-23-02]EN
cyclic rating factor
factor by which the permissible steady-state rated current corresponding to a 100 % load factor may be multiplied to obtain the permissible peak value of current during a daily cycle such that the conductor attains, but does not exceed, the maximum rated temperature during the cycle
[IEV number 461-23-02]FR
facteur de régime cyclique
facteur par lequel le courant assigné admissible en régime permanent, correspondant à un facteur de charge 100 %, peut être multiplié pour obtenir la valeur de pointe du courant au cours d'un cycle journalier, de sorte qu'au cours de ce cycle, l'âme atteigne sans la dépasser la température assignée maximale
[IEV number 461-23-02]Тематики
- кабели, провода...
EN
DE
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > facteur de régime cyclique
-
7 puissance disponible d'une centrale
располагаемая мощность агрегата (электростанции)
Установленная мощность генерирующего агрегата (электростанции), за вычетом ограничений его мощности.
[ ГОСТ 19431-84]EN
available capacity of a unit
the maximum power at which a unit can be operated continuously under the prevailing conditions
Note – This power may be gross or net.
[IEV ref 602-03-11]
available capacity of a power station
the maximum power at which a power station can be operated continuously under the prevailing conditions
Note – This power may be gross or net.
[IEV ref 602-03-12]FR
puissance disponible d'une tranche
puissance maximale réalisable en régime continu dans les conditions réelles où une tranche se trouve
Note – Cette puissance peut être brute ou nette.
[IEV ref 602-03-11]
puissance disponible d'une centrale
puissance maximale réalisable en régime continu dans les conditions réelles où une centrale se trouve
Note – Cette puissance peut être brute ou nette.
[IEV ref 602-03-12]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
DE
- verfügbare Leistung eines Blocks, f
- verfügbare Leistung eines Kraftwerks
FR
- puissance disponible d'une centrale
- puissance disponible d'une tranche
- puissance disponible d’une centrale
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > puissance disponible d'une centrale
-
8 puissance disponible d'une tranche
располагаемая мощность агрегата (электростанции)
Установленная мощность генерирующего агрегата (электростанции), за вычетом ограничений его мощности.
[ ГОСТ 19431-84]EN
available capacity of a unit
the maximum power at which a unit can be operated continuously under the prevailing conditions
Note – This power may be gross or net.
[IEV ref 602-03-11]
available capacity of a power station
the maximum power at which a power station can be operated continuously under the prevailing conditions
Note – This power may be gross or net.
[IEV ref 602-03-12]FR
puissance disponible d'une tranche
puissance maximale réalisable en régime continu dans les conditions réelles où une tranche se trouve
Note – Cette puissance peut être brute ou nette.
[IEV ref 602-03-11]
puissance disponible d'une centrale
puissance maximale réalisable en régime continu dans les conditions réelles où une centrale se trouve
Note – Cette puissance peut être brute ou nette.
[IEV ref 602-03-12]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
DE
- verfügbare Leistung eines Blocks, f
- verfügbare Leistung eines Kraftwerks
FR
- puissance disponible d'une centrale
- puissance disponible d'une tranche
- puissance disponible d’une centrale
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > puissance disponible d'une tranche
-
9 puissance disponible d’une centrale
располагаемая мощность агрегата (электростанции)
Установленная мощность генерирующего агрегата (электростанции), за вычетом ограничений его мощности.
[ ГОСТ 19431-84]EN
available capacity of a unit
the maximum power at which a unit can be operated continuously under the prevailing conditions
Note – This power may be gross or net.
[IEV ref 602-03-11]
available capacity of a power station
the maximum power at which a power station can be operated continuously under the prevailing conditions
Note – This power may be gross or net.
[IEV ref 602-03-12]FR
puissance disponible d'une tranche
puissance maximale réalisable en régime continu dans les conditions réelles où une tranche se trouve
Note – Cette puissance peut être brute ou nette.
[IEV ref 602-03-11]
puissance disponible d'une centrale
puissance maximale réalisable en régime continu dans les conditions réelles où une centrale se trouve
Note – Cette puissance peut être brute ou nette.
[IEV ref 602-03-12]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
DE
- verfügbare Leistung eines Blocks, f
- verfügbare Leistung eines Kraftwerks
FR
- puissance disponible d'une centrale
- puissance disponible d'une tranche
- puissance disponible d’une centrale
52. Располагаемая мощность агрегата (электростанции)
Располагаемая мощность
E. Available power station capacity
F. Puissance disponible d’une centrale
Установленная мощность генерирующего агрегата (электростанции), за вычетом ограничений его мощности
Источник: ГОСТ 19431-84: Энергетика и электрификация. Термины и определения оригинал документа
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > puissance disponible d’une centrale
-
10 courant admissible, m
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > courant admissible, m
-
11 courant permanent admissible, m
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > courant permanent admissible, m
-
12 pression
f1) давление2) напор; напряжение; усилие3) нагнетание•- pression active
- pression admissible
- pression d'alimentation
- pression amont
- pression en amont
- pression en amont de pompe
- pression annulaire
- pression dans l'annulaire tubage
- pression anormale
- pression d'appui
- pression artésienne
- pression d'aspiration
- pression atmosphérique
- pression aval
- pression en aval
- basse pression
- pression de boue
- pression de bulle
- pression capillaire
- pression de chute
- pression de cimentation finale
- pression dans la colonne
- pression en colonne d'eau
- pression de la colonne lithologique
- pression de compaction
- pression de condensation
- pression de consolidation
- pression de couche
- pression des couches sus-jacentes
- pression critique
- pression de cuvelage
- pression dans l'espace tubing-tubage
- en débit
- pression de débit
- pression de déplacement
- pression différentielle
- pression dirigée
- pression de dissolution
- pression due au poids des sédiments
- pression d'eau
- pression de l'eau interstitielle
- pression d'écoulement
- pression effective
- pression d'épreuve
- pression d'éruption
- pression d'éruption d'un puits
- pression dans l'espace annulaire
- pression d'essai
- pression excédentaire
- pression exercée par les terrains sus-jacents
- pression d'exploitation
- pression de filtration
- pression finale
- pression de fond
- pression de fond en débit
- pression de fond en fermeture
- pression de fond en puits fermé
- pression en fond de trou finale
- pression de fond statique pour un puits fermé
- pression de formation
- pression de fracturation
- pression du gaz
- pression du gaz à la sortie du gazomètre
- pression gazométrique
- pression géodynamique
- pression géostatique
- pression de gisement
- pression de gisement en écoulement naturel
- pression de gisement à la limite d'épuisement
- pression de gonflement
- haute pression
- pression hydrostatique
- pression hydrostatique finale de la boue
- pression hydrostatique initiale de la boue
- pression initiale
- pression initiale d'écoulement
- pression initiale de réservoir
- pression d'injection
- pression d'injection superficielle
- pression interstitielle
- pression d'introduction
- pression latérale
- pression de ligne
- pression limite
- pression manométrique
- pression maximum
- pression maximum de stockage
- pression minimum
- pression de miscibilité
- pression moyenne de la couche
- pression oléostatique
- pression opératoire
- pression originelle de réservoir
- pression orogénique
- pression osmotique
- pression sur outil
- pression d'ouverture
- pression partielle
- pression pseudocritique
- pression réduite
- pression de refoulement
- pression de régime
- pression de remplissage
- pression de réservoir
- pression résiduelle de l'eau interstitielle
- pression de rosée rétrograde
- pression au sabot
- pression de saturation
- pression de séparateur
- pression de seuil
- pression du sol au repos
- pression au sondage
- pression à la sortie de pompe
- pression statique de la colonne de liquide
- pression statique de fond
- pression statique de la tête de puits
- pression supportée
- pression de surcharge
- pression de terrains
- pression en tête de l'espace annulaire
- pression en tête de puits
- pression en tête du tubage
- pression du toit
- pression variable
- pression à vide
- pression vierge de gisement
- pression de voûte -
13 marche
I f1) ход; движениеen état de marche — на ходу (об оборудовании, аппаратуре), действующий
mettre en marche — приводить в движение, пускать в ход
mettre hors de marche — останавливать, прекращать действие
en ordre de marche — готовый к эксплуатации, готовый к пуску
2) работа; процесс; действие3) ступень, ступенька; подножка4) педаль5) мат. блуждание•- marche par à-coups
- marche arrière
- marche en arrière
- marche automatique
- marche avant
- marche en avant
- marche à blanc
- marche de la chauffe
- marche sans chocs
- marche du circuit d'eau
- marche de combustion
- marche à combustion modulable
- marche à condensation
- marche continue du laser
- marche à contre-pression
- marche douce
- marche à droite
- marche économique
- marche équilibrée
- marche d'escalier
- marche fonctionnelle
- marche de fourneau
- marche à froid
- marche à gauche
- marche à gaz pauvre
- marche à gaz riche
- marche par inertie
- marche interconnectée
- marche en interconnexion
- marche intermittente
- marche au moteur
- marche à moteur débrayé
- marche non surveillée
- marche normale
- marche optique
- marche en parallèle
- marche partielle
- marche en pleine charge
- marche au ralenti
- marche des rayons
- marche à régime établi
- marche régulière
- marche en sens inverse
- marche silencieuse
- marche sur son erre
- marche en surcharge
- marche symétrique
- marche en travail
- marche uniforme
- marche à vide
- marche à la vitesse maximum II "marche"включённый; "включено" -
14 puits
mскважина, буровая скважинаarrêter un puits — останавливать скважину, закрывать скважину
faire produire un puits au maximum de sa capacité — пускать скважину на свободный дебит, эксплуатировать скважину на режиме максимальной производительности
reprendre un puits — вновь осваивать скважину; разбуривать цементную пробку для продолжения бурения
- puits absorbanttuer un puits — задавливать скважину или пластовое давление
- puits achevé
- puits actif
- puits en activité
- puits adjacent
- puits d'alimentation
- puits d'alimentation d'eau
- puits d'alimentation du gas-cap
- puits anhydre
- puits artésien
- puits avarié
- puits à balancier
- puits bon producteur
- puits de bordure
- puits bouché
- puits capricieux
- puits commercial
- puits à complétion multiple
- puits de condensat
- puits de confirmation
- puits creusé à la main
- puits curé
- puits à débit intermittent
- puits débitant par l'espace annulaire
- puits débitant par le tubing
- puits découvert
- puits de découverte
- puits à deux colonnes
- puits à deux horizons productifs
- puits de développement
- puits à déviation double
- puits dévié
- puits dirigé
- puits disposé en quinconce
- puits de doublement
- puits droit
- puits d'eau
- puits d'eau salée
- puits d'eau saumâtre
- puits à l'écoulement naturel
- puits épuisé
- puits éruptif
- puits en éruption
- puits à éruption intermittente non contrôlée
- puits d'essai
- puits d'exploitation
- puits d'exploration
- puits d'extension
- puits d'extraction
- puits à faible index de productivité
- puits à faible producteur
- puits fermé
- puits de flanc
- puits de forage
- puits foré au câble
- puits foré dans un réservoir reconnu productif
- puits à fort index de productivité
- puits fou
- puits en gas lift continu
- puits en gas lift intermittent
- puits à gaz
- puits de gaz
- puits de gaz en éruption
- puits de gaz productif
- puits à haute pression
- puits horizontal
- puits d'huile
- puits à huile éruptif
- puits d'huile productif
- puits improductif
- puits incliné
- puits inframarginal
- puits injecteur
- puits d'injection
- puits d'injection d'air
- puits d'injection d'eau
- puits d'injection de gaz
- puits injection-production
- puits inondé
- puits d'intervention
- puits isolé
- puits jaillissant
- puits à jaillissement intermittent
- puits jalonnant les limites de productivité d'un gisement
- puits jumelé
- puits latéral
- puits de limite
- puits à la limite d'un gisement
- puits en lisière
- puits à main
- puits marginal
- puits mauvais producteur
- puits mouillé
- puits naturel
- puits en nettoyage
- puits non commercial
- puits non éruptif
- puits non tubé
- puits noyé
- puits d'obligation
- puits oblique
- puits d'observation
- puits obtenu par forage dirigé
- puits offshore
- puits payant
- puits à pénétration partielle
- puits à pénétration totale
- puits périphérique
- petit puits
- puits de petit diamètre
- puits à pétrole
- puits de pétrole
- puits pétrolier
- puits peu profond
- puits piézométrique
- puits en pistonnage
- puits plein
- puits en pompage
- mettre un puits en pompage
- puits en pompage par dispositif à balancier
- puits pompé
- puits producteur
- puits producteur d'eau
- puits producteur d'eau et d'huile
- puits producteur d'eau et de pétrole
- puits producteur de gaz
- puits producteur d'huile
- puits producteur de pétrole
- puits de production
- puits en production
- mettre un puits de production
- mettre un puits en production
- puits hors production
- puits à production forcée
- puits à production par pompage
- puits produisant par annulaire
- puits produisant par l'espace annulaire
- puits produisant du gaz
- puits produisant goutte à goutte
- puits produisant à partir des horizons différents
- puits profond
- puits provisoirement fermé
- puits en puisage
- puits en quinconce
- puits de recherche
- puits reconditionné
- puits de reconnaissance
- puits de recyclage
- puits de référence
- puits de refoulement
- puits à régime pulsatif
- puits de réinjection d'eau salée
- puits remis en production
- puits rentable
- puits salé
- puits satellite
- puits sec
- puits de secours
- puits de sommet
- puits sous-marin
- puits de soutirage
- puits stérile
- puits stimulé
- puits de stockage souterrain
- puits témoin
- puits thermométrique
- puits tubé
- puits tué
- puits ultraprofond
- puits vertical -
15 R.M.C.
сущ.тех. régime maximum continu -
16 R.M.R.
сущ. -
17 glaciaire
гляциальный; ледниковый* -
18 pression
f1. давление □ basse pression низкое давление; пониженное давление; haute pression высокое давление; résister à pression сопротивляться давлению; сопротивляться выдавливанию (напр. при смазке) 2. усилиеpression à l'admission — давление при впуске; давление на входеpression d'assemblage — усилие посадки при сборке; усилие прижатия (соединяемых поверхностей)pression de calage — давление при насаживании, давление запрессовки или напрессовки; давление при посадке с натягомpression de calcul — расчётное давление; расчётный напорpression de compression — давление сжатия; усилие сжатияpression de contact — 1. контактное давление 2. удельное давление (напр. на цапфу)pression critique — критическое давление; критический напорpression disponible — рабочее [фактическое] давлениеpression de distribution — давление при подаче (напр. сжатого воздуха)pression dynamique — динамическое давление; скоростной напорpression d'écrasement — давление, вызывающее смятиеpression effective — манометрическое [избыточное] давлениеpression à l'entrée — давление на входе; давление при впускеpression d'étanchéité — давление, обеспечивающее герметичностьpression de fluide — давление среды, рабочее давление (гидравлического пресса)pression locale — местное давление; местное напряжениеpression oscillante — переменное [колеблющееся] давлениеpression sur palier — давление [нагрузка] на подшипникpression portante — грузоподъёмность; несущая способность (конструкции)pression réduite — 1. приведённое давление 2. пониженное давлениеpression à la sortie — давление на выходе; давление при выпускеpression de soudage — (рабочее) давление при сваркеpression sur les surfaces travaillantes — давление на рабочие поверхности (напр. кулачков) -
19 puissance
fpuissance absorbée par la coupe — (эффективная) мощность резанияpuissance absorbée effectivement — эффективная [полезная] мощностьpuissance d'appareil — 1. мощность устройства или приспособления 2. разрешающая способность прибораpuissance de déformation — мощность, затрачиваемая на деформирование; усилие деформацииpuissance effective — эффективная [полезная] мощностьpuissance fournie — подводимая мощность; мощность на валуpuissance fournie par la machine — мощность, развиваемая машинойpuissance au frein — тормозная мощность; мощность на валуpuissance de freinage — тормозная мощность; мощность на валуpuissance hydraulique — мощность потока жидкости, гидравлическая мощностьpuissance importante — высокая мощность; высокая производительностьpuissance de la machine — мощность машины или станка; производительность машины или станкаpuissance motrice — 1. мощность на валу; мощность привода 2. движущая силаpuissance perdue par frottement — мощность, затраченная на трениеpuissance portante — 1. грузоподъёмность (напр. крана) 2. несущая способность (напр. подшипника)puissance totale — суммарная [полная] мощность; суммарное усилиеpuissance totale fournie — полная отдаваемая [рабочая] мощностьpuissance utile à l'outil — полезная мощность на резце; полезная мощность инструмента -
20 facteur de qualité
добротность
1. Количественная характеристика потерь колебательной системы при резонансе, равная
где Wк - полный запас энергии колебаний при резонансе;
Wп - потери энергии за период
[ Физический энциклопедический словарь]
2. Количественная мера потерь колебательной системы. Показывает, во сколько раз амплитуда вынужденных колебаний при резонансе превышает амплитуду на частоте, много меньшей резонансной при одинаковой внешней силе
3. Отношение резонансной частоты спектра колебаний к его ширине на уровне 0,707 от максимального значения амплитуды спектра
Примечание
Определения 2 и 3 являются достаточно точными для систем с высокой добротностью (Q >(5-10)), определение 1 пригодно во всех случаях
[Система неразрушающего контроля. Виды (методы) и технология неразрушающего контроля. Термины и определения (справочное пособие). Москва 2003 г.]
добротность (1)
коэффициент добротности (1)
-
[IEV number 151-15-45]
добротность (2)
коэффициент добротности (2)
-
[IEV number 151-15-46]EN
quality factor (1)
Q factor (1)
for a capacitor or inductor under periodic conditions, ratio of the absolute value of the reactive power to the active power
NOTE 1 – The quality factor is a measure of the losses, usually unwanted, in a capacitor or an inductor.
NOTE 2 – The quality factor depends generally on frequency and voltage.
[IEV number 151-15-45]
quality factor (2)
Q factor (2)
for a resonant circuit at the resonance frequency, 2π times the ratio of the maximum stored energy to the energy dissipated during one period
NOTE – The quality factor is a measure of sharpness of the resonance.
Source: 801-24-12 MOD
[IEV number 151-15-46]FR
facteur de qualité (1), m
facteur de surtension (1), m
pour un condensateur ou une bobine d'inductance en régime périodique, rapport de la valeur absolue de la puissance réactive à la puissance active
NOTE 1 – Le facteur de qualité caractérise les pertes, généralement non désirées, dans un condensateur ou une bobine d'inductance.
NOTE 2 – Le facteur de qualité dépend généralement de la fréquence et de la tension.
[IEV number 151-15-45]
facteur de qualité (2), m
facteur de surtension (2), m
pour un circuit résonant fonctionnant à la fréquence de résonance, 2π fois le rapport de l'énergie maximale emmagasinée dans le circuit à l'énergie dissipée pendant une période
NOTE – Le facteur de qualité caractérise l'acuité de la résonance.
Source: 801-24-12 MOD
[IEV number 151-15-46]Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
добротность конденсатора
Отношение реактивной мощности конденсатора к его активной мощности при синусоидальном напряжении определенной частоты.
[ ГОСТ 21415-75]
добротность конденсатора
-
[Лугинский Я. Н. и др. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике. 2-е издание - М.: РУССО, 1995 - 616 с.]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
D. Gütefaktor
E. Quality factor
F. Facteur de qualité
Отношение реактивной мощности конденсатора к его активной мощности при синусоидальном напряжении определенной частоты
Источник: ГОСТ 21415-75: Конденсаторы. Термины и определения оригинал документа
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > facteur de qualité
- 1
- 2
См. также в других словарях:
maximum — [ maksimɔm ] n. m. • 1718; mot lat. « le plus grand » 1 ♦ Math. Valeur d une fonction supérieure à celles qui la précèdent ou la suivent immédiatement. Premier, second maximum d une fonction, d une courbe, d un graphique. ⇒ pointe. 2 ♦ (1751)… … Encyclopédie Universelle
Regime de retraite des artisans francais — Régime de retraite des artisans français Le régime de retraite des artisans est rattaché depuis le 1er juillet 2006 au Régime social des indépendants (RSI). Création en 1948 du régime d assurance vieillesse des artisans (AVA) géré par la Caisse… … Wikipédia en Français
Regime de retraite des commercants francais — Régime de retraite des commerçants français Le régime de retraite des commerçants français est un régime français concernant les travailleurs indépendants du commerce, de l industrie et des services et les entreprises de plus de 10 salariés… … Wikipédia en Français
régime — 1. régime [ reʒim ] n. m. • 1408; regisme « royaume » 1190; lat. regimen « action de diriger » → régir 1 ♦ Vx Façon d administrer, de gouverner une communauté. Par ext. (1789) Mod. Organisation politique, économique, sociale d un État. ⇒ système … Encyclopédie Universelle
Maximum sustainable yield — In population ecology and economics, maximum sustainable yield or MSY is, theoretically, the largest yield (or catch) that can be taken from a species stock over an indefinite period. Fundamental to the notion of sustainable harvest, the concept… … Wikipedia
Régime de Vichy — Pour les articles homonymes, voir Vichy (homonymie) et État français (homonymie). État français Régime de Vichy … Wikipédia en Français
Régime spécial de retraites — Régimes spéciaux de retraite En France, les régimes spéciaux de retraite sont des régimes de retraite dont bénéficient des employés de certaines grandes entreprises publiques, (SNCF, RATP), ou de branches entières comme celle des Industries… … Wikipédia en Français
Régime spécial des retraites — Régimes spéciaux de retraite En France, les régimes spéciaux de retraite sont des régimes de retraite dont bénéficient des employés de certaines grandes entreprises publiques, (SNCF, RATP), ou de branches entières comme celle des Industries… … Wikipédia en Français
Régime Dukan — Le régime Dukan (aussi appelé régime Protal pour protéine et alternance) est un régime amaigrissant mis au point par le docteur Pierre Dukan[1]. Sommaire 1 Principe 2 Efficacité … Wikipédia en Français
Régime enregistré d'épargne-études — Le régime enregistré d épargne études (REEE) permet aux épargnes pour les études de croître à l abri de l impôt dans un régime d épargne spécial enregistré par le Gouvernement du Canada jusqu à ce que l enfant nommé dans le REEE s inscrive à un… … Wikipédia en Français
Régime de neutre — Schéma de liaison à la terre Pour les articles homonymes, voir SLT. En électricité, un Schéma de Liaison à la Terre, ou SLT (Anciennement Régime de neutre) définit le mode de raccordement à la terre du point neutre d un transformateur de… … Wikipédia en Français